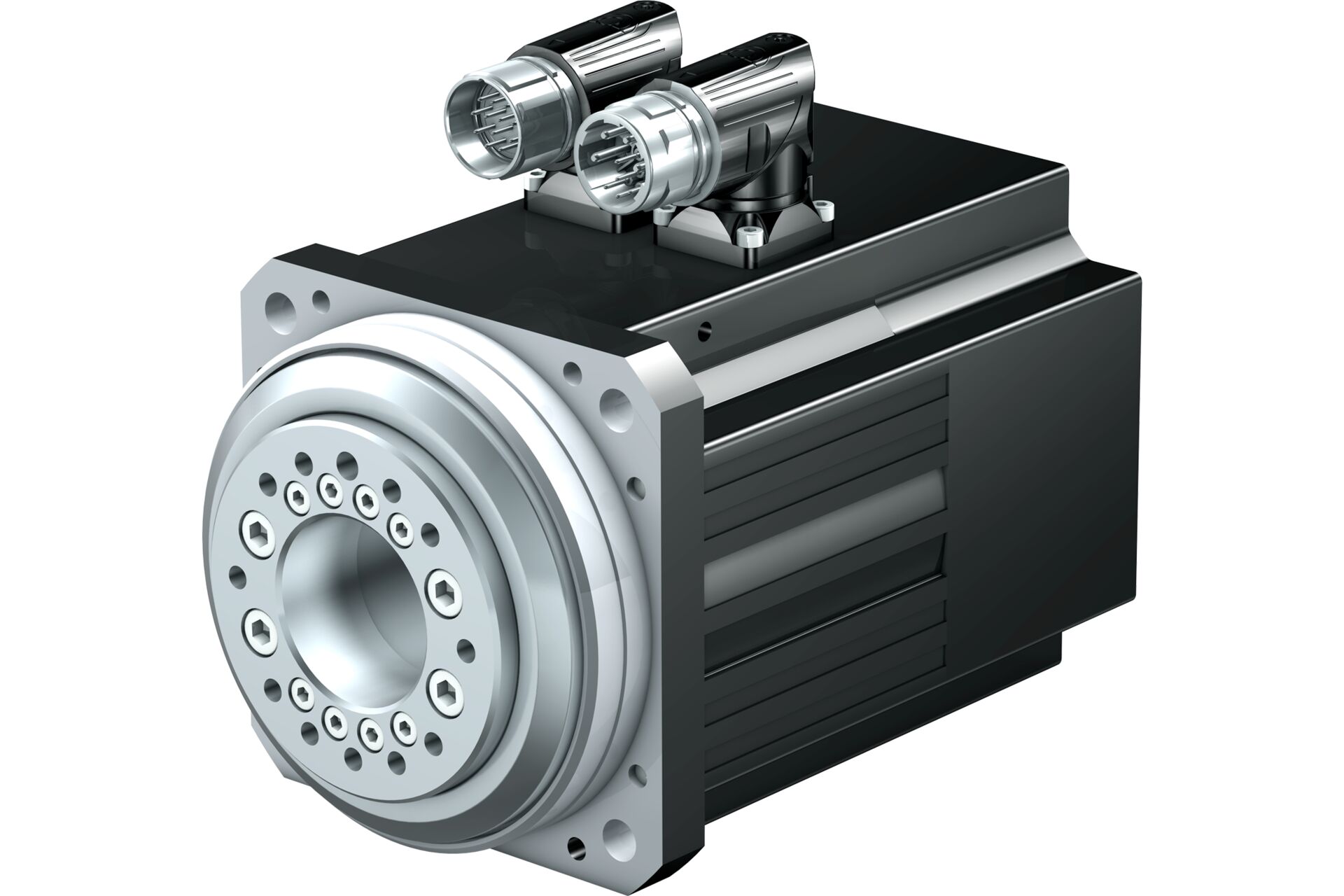
Servo motors are preervo motors are precision-engineered devices designed to deliver accurate control over position, speed, and acceleration. They utilize advanced feedback systems, which set them apart from other motor types like stepper and DC motors. Unlike these alternatives, servo motors excel in complex motion tasks, thanks to their dynamic feedback loops that ensure high accuracy.
Servo motors play a vital role in industries such as robotics and automation, where precision and repeatability are critical. From assembling intricate components to precise positioning and control, servo motors enable modern innovations by meeting demanding industrial requirements with unmatched efficiency and reliability.
What is a servo motor?
A servo motor consists of several key components that work together to achieve precision and control:
- Motor (DC or AC): Generates the rotational movement.
- Gearbox: Modifies torque and speed to match application needs.
- Feedback Device (Encoder or Potentiometer): Continuously monitors the motor’s position and speed.
- Servo Controller: Adjusts performance based on real-time feedback to maintain accuracy.
- Power Supply: Provides the energy necessary for consistent operation.
Each component’s functionality contributes to the servo motor’s precise movements. For example, the encoder detects even the smallest positional changes and relays this data to the servo controller. The controller then uses this information to fine-tune the motor’s output, ensuring the desired performance is consistently met. Our experts are ready and willing to help you find the right solution for your load capacity, torque demands and operational conditions.
How does a servo motor work?
Servo motors achieve their precision through a sophisticated feedback loop. When an input signal is sent to the motor, the controller interprets the control signal and generates a response. This response is continuously adjusted by the feedback mechanism, which monitors the motor’s position and speed.
Most servo motors rely on closed-loop control systems that utilize Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signals. These signals dictate the motor’s output, allowing precise adjustments to achieve the required position. The feedback device, such as an encoder, ensures that real-time data is relayed to the controller, which compensates for any deviations from the desired outcome. This seamless process demonstrates how servo motors work with high precision and reliability, even in demanding applications.
Servo motors vs. other motor types
Servo motors are just one type of motor commonly found in industrial equipment. Each variety has its own set of strengths and weaknesses, but servos often outstrip other types for a number of reasons. Here’s how a servo motor stacks up compared to some of the most common alternatives:
- Stepper motors: Steppers are known for being relatively inexpensive and being able to operate in open-loop systems. However, they also have a tendency to miss steps and lose torque at higher speeds. On the other hand, servo motors use closed-loop feedback to ensure accuracy under load as well as maintain torque at higher RPMs. This makes servo motors more reliable for demanding automation applications.
- Induction motors: Although induction motors perform very well in constant-speed applications such as pumps and fans, they lack precision control over acceleration or stopping points. Servos, in comparison, offer the variable-speed, position-control capabilities needed for robotics, CNC and high-precision automation.
- DC motors: Simple and affordable, DC motors nevertheless are prone to wear due to the brushes they contain and offer limited precision. With servos, however, operators can experience longer lifespans, less maintenance and higher accuracy in mission-critical environments. This is especially true of brushless AC servo motors.
It’s no wonder servo motors are the dominant choice in applications that demand high degrees of precision and control, such as in robotic arms, CNC machining and pick-and-place systems. In other cases, though, a different type of motor may provide performance that is good enough to meet the demands of the task.
Types of servo motors
Servo motors come in several types, each suited to specific applications:
- DC servo motor: Simple and effective for low-to-medium speed applications, such as conveyor belts and hobby robotics.
- AC servo motor: Known for their efficiency and high torque output, they excel in industrial and high-performance tasks like CNC machining.
- Brushless servo motors: Offer minimal wear and maintenance with higher efficiency, ideal for environments requiring high precision and long service life.
- Stepper motors: While technically not servo motors, stepper motors provide precise, discrete positioning and are often used in applications where high accuracy is necessary without feedback loops.
Choosing the right servo motor
Choosing the right servo motor involves considering factors like torque, speed, power, size, feedback requirements, and environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity. The motor’s specifications must align with the application’s needs—high precision is essential in robotics, while durability is critical in industrial automation. For example, aerospace applications demand precise control, while manufacturing environments require motors built for long-lasting performance. Matching the motor to the specific demands of each industry ensures optimal efficiency and reliability.
Common mistakes when choosing a servo motor
Unfortunately, operators often neglect some critical considerations when choosing a servo motor. This can lead to a host of issues that impact productivity and efficiency. Some of the most common mistakes to avoid include:
- Undersizing for torque and power: If a motor only handles average loads but not peak torque, it can lead to overheating, lost accuracy and premature wear.
- Ignoring duty cycle: Using a motor rated for intermittent operation in continuous high-speed systems will lead to early failure.
- Overlooking feedback requirements: Applications that call for micron-level accuracy need equally high-resolution encoders. If operators settle for lower-cost options, it can result in errors or quality assurance failures.
- Misjudging integration needs: If a standalone servo is chosen without consideration for the gearbox compatibility of drive/controller requirements, it can result in a much more difficult installation.
To avoid mistakes like these, it’s critical to consult engineering support from the manufacturer, use product configuration tools and validate specs against the actual operating environment.
Applications of servo motors
- Robotics: Drive robotic arms for precise, repeatable tasks like picking and placing objects.
- CNC machines: Control cutting tools to ensure accurate machining and material shaping.
- Aerospace: Adjust flight-critical components, such as wings and flaps, with fine-tuned control.
- Industrial automation: Operate conveyor belts and assembly lines, ensuring speed, precision, and efficiency.
Applications of servo motors
- Robotics: Drive robotic arms for precise, repeatable tasks like picking and placing objects.
- CNC machines: Control cutting tools to ensure accurate machining and material shaping.
- Aerospace: Adjust flight-critical components, such as wings and flaps, with fine-tuned control.
- Industrial automation: Operate conveyor belts and assembly lines, ensuring speed, precision, and efficiency.
Industry-specific servo motor applications
- Medical devices: Surgical robots, imaging systems and diagnostic equipment require high levels of precision. Servo motors provide ultra-low levels of vibration and exceptional repeatability while also meeting regulatory requirements for sterility and safety.
- Packaging and printing: Servo motors can support high-speed cycles, accurate indexing and multi-axis synchronization, making them perfect for modern packaging and labeling equipment where downtime also must be kept at a minimum.
- Renewable energy: Servos can optimize panel alignment in solar tracking systems, control pitch adjustment in wind turbines and generally withstand the rigors of outdoor environments.
- Automotive: Servo motors are used to drive test benches, support EV battery assembly and support control systems such as adaptive steering or active suspension. Their ability to provide torque accuracy under dynamic conditions is especially important here.
- Industrial automation: In assembly lines and conveyor systems, servo motors deliver repeatable motion while enabling scalability for future automation upgrades.
Advantages of servo motors
Servo motors offer several benefits that make them the preferred choice for high-precision applications:
- Precise control: Position, speed, and acceleration are managed with exceptional accuracy.
- High torque: Compact motors deliver significant force for both light and heavy-duty tasks.
- Energy efficiency: High-precision servo motors reduce power consumption without sacrificing performance.
- Compact design: Their small size enables use in tight spaces and intricate systems.
Maintenance and reliability of servo motors
Keeping servo motors in prime working order is crucial for ensuring their reliability across all applications. Proper maintenance practices for servos include:
- Routine inspections: Wiring, encoder connections and housings should be inspected regularly to check for signs of wear or contamination. Even small issues like loose cables can cause feedback loss or intermittent faults that can harm performance.
- Lubrication and pairing with gearboxes: When servo motors are paired with gearboxes, lubrication is essential. Servos benefit from sealed or lubed-for-life systems like STOBER gearboxes to eliminate the risk of lubrication errors.
- Condition monitoring: With the use of thermal imaging, vibration analysis and current draw measurements, operators can spot the early warning signs of failure.
- Environmental awareness: Housings and seals for servos should be selected with an understanding the environmental conditions in which they will be used.
- Proactive maintenance: With preventive care, servo motors can benefit from extended service life, minimized downtime and guaranteed efficiency.
The future of servo motors
Servo motors are vital for precise motion control, making them indispensable in robotics, aerospace, and industrial automation. Advancements in efficient designs, enhanced feedback loops, and improved materials are driving the future of automation and robotics. STOBER leads the industry with innovative servo motor and gearbox solutions tailored to modern demands.
Integration with gearboxes and servo drives
ntegrating a servo motor with the proper gearbox and drive is key for achieving the highest levels of performance and efficiency. STOBER’s complete range of gearbox solutions complement our servo motors to offer the best possible experience for industrial users. For instance, pairing a servo with our planetary or helical gearboxes enable higher torque density and smoother motion while reducing motor size requirements.
A complete integrated STOBER system consisting of a servo motor, gearbox and drive ensures components are tolerance-matched, reducing the chances of misalignment or assembly issues. These systems also minimize their footprint, giving designers the ability to fit motors into tight or complex assemblies without compromising performance. With sealed lubrication and lubed-for-life designs, these also simplify maintenance and reduce downtime. Our systems can be found in CNC machining centers, robotics systems and packaging lines thanks to their precision, space-saving designs and reliability.
For engineers and automation specialists, understanding servo motor functionality is crucial for improving performance, efficiency, and precision in an evolving technological landscape.
To discover the right solutions for your needs, explore products now or contact us to explore industries where servo motors make an impact.
Learn more about STOBER product options by clicking the link below or contact us at (888) 786-2371 or email sales@stober.com.






 Selecting gearboxes for robotic & industrial automation systems
Selecting gearboxes for robotic & industrial automation systems  Horizontal mounting without the headaches: How STOBER makes it simple
Horizontal mounting without the headaches: How STOBER makes it simple  What causes gearbox failure? Key causes & early warning signs
What causes gearbox failure? Key causes & early warning signs  Gearbox noise reduction: Causes, fixes & best practices
Gearbox noise reduction: Causes, fixes & best practices